Now that check_mk is installed, we'll enable monitoring its own host by installing the check_mk agent. While the agent can be queried through various means, the regular way is by making it accessible through xinetd, so we install that first:
- Code:
-
yum install xinetd
Then we only need to copy the agent script check_mk_agent.linux to /usr/bin/check_mk_agent and the xinetd configuration file xinetd.conf to /etc/xinetd.d/check_mk:
- Code:
-
cp -p /usr/share/check_mk/agents/check_mk_agent.linux /usr/bin/check_mk_agent
cp -p /usr/share/check_mk/agents/xinetd.conf /etc/xinetd.d/check_mk
/etc/init.d/xinetd restart
Une petite vérification pour voir si le démon est en écoute sur le port 6556 par défaut.
- Code:
-
netstat -ltn
- Citation :
- Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6556 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN
Il reste à tester le démon en l'interrogeant avec check_mk
- Code:
-
check_mk -I alltcp localhost
Le démon découvre alors les services associé à la machine
- Citation :
- No new checks of type oracle_asm_dg.
No new checks of type vms_md.
1 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/cpu.loads-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
No new checks of type lsi.disk.
No new checks of type statgrab_net.link.
No new checks of type statgrab_net.params.
No new checks of type oracle_tbs.
No new checks of type multipath.
1 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/cpu.threads-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
2 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/diskstat-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
No new checks of type winperf.cpuusage.
No new checks of type vms_sys.mem.
No new checks of type local.
No new checks of type statgrab_net.ctr.
No new checks of type lsi.array.
No new checks of type vms_df.
2 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/df-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
No new checks of type ipmi.
1 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/mem.used-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
1 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/netif.params-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
No new checks of type services.
No new checks of type tsm_stgpool.
No new checks of type winperf.diskstat.
No new checks of type vms_sys.util.
1 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/netctr.combined-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
No new checks of type md.
1 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/kernel.util-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
No new checks of type oracle_inst.
No new checks of type logwatch.
1 new checks written to /var/lib/check_mk/autochecks/netif.link-2009-04-28_10.00.58.cfg
No new checks of type oracle_asm_disk.
No new checks of type vms_netif.
L'installation est finie.
Installation de l'agent sous windows
Sous windows l'installation est vraiment triviale. A l'intérieur de l'archive “source” vous trouverez une archive agents.tar.gz. Il suffit d'extraire le contenu de l'archive et de transférer le fichier check_mk_agent.exe sur un serveur windows (par exemple dans le répertoire c:\check_mk.
L'invocation de check_mk en ligne de commande avec l'argument –help nous donne le résultat suivant :

L'installation en mode service se fait donc de la manière suivante :
- Code:
-
check_mk_agent.exe install
Il ne reste plus qu'a démarrer le service grâce à la console de gestion des services windows (Menu démarrer → exécuter → services.msc).

Un petit test pour vérifier que tout se passe bien :
- Code:
-
check_mk_agent.exe test
Utilisation
- Code:
-
check_mk -nv localhost
- Citation :
- Getting info cpu from host localhost (127.0.0.1)
CPU load OK - 0.02
Number of threads OK - 76 threads
fs_/ OK - 4% used
fs_/boot OK - 15% used
Disk IO read OK - 0.0MB/s (in last 1240909505 secs)
Disk IO write OK - 0.0MB/s (in last 1240909505 secs)
CPU utilization OK - user: 0%, system: 0%, wait: 4%
Memory used OK - 31.3% of RAM (157 MB) used by processes
NIC eth0 counters OK - Receive: 0.00 MB/sec - Send: 0.00 MB/sec
NIC eth0 link OK - Link is up
NIC eth0 parameter OK - 1000Mb/s,Full,off
OK - Version 16, Successfully processed 11 host infos
Voici l'écran d'aide la commande check_mk
- Citation :
- Usage:
MAJOR MODES:
check_mk [-n] [-v] [-p] HOST [IPADDRESS] perform host checks
check_mk -S|-H output configuration files for Nagios
check_mk -C precompile host checks
check_mk -d HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS show plain information from agent
check_mk -I df [HOST1 HOST2...] Inventory of mounted partitions
OPTIONS:
-c FILE read config file FILE instead of /etc/check_mk/check_mk.cfg
-S output service configuration for Nagios
-H output host configuration for Nagios
-C, --compile precompile host checks (into /var/lib/check_mk/precompiled/)
-L list all available check types
-v, --verbose verbose output, for manual testing
--cache read info from cache file is present, use TCP only,
if no cache file present
--no-cache never use cached information (use *before* -I)
-p also show performance data (use with -v)
-n do not submit results to Nagios, do not save counters
-d just show ouput from agent, do not perform checks
-I type1,type2,.. make inventory of one or more checktypes.
Use '-L' or '-I list' for list of check types available
for inventory. Use '-I alltcp' for inventory on
all checks based on mknagios (and leave out SNMP)
--no-tcp for -I: only use cache files. Skipt hosts without
cache files.
--list-hosts [G1 G2 G3...] output all hostnames or only those
contained in one of a list of hostgroups
-h, --help print this help
-V, --version print version and exit
If called without options check_mk retrieves information about host
at IPADDRESS via TCP or SNMP and submits passive check results to
Nagios for all services configured in /etc/check_mk/check_mk.cfg for that host.
Intégration avec Nagios - Citation :
- L'agent check_mk doit être installé sur chacune de vos machines.
Vous devrez créer l'utilisateur nagios pour pouvoir faire l'inventaire.
- Code:
-
sudo adduser nagios
- Citation :
- Sur vos hôtes distants check_mk ne trouvera pas Nagios, répondez par défaut au question ce n'est pas grave, cette partie n'est utile que lors du poussage de la configuration.
ConfigurationSur le serveur Nagios configurer le fichier /etc/check_mk/main.mk
S'il n'y a que le serveur nagios, l'éditer comme ci-dessous :
- Citation :
- all_hosts = [ 'localhost' ]
Si d'autres hôtes viennent à être supervisés:
- Citation :
- all_hosts = [ 'localhost', 'hote-ubuntu' ]
Vous pouvez renseigner des noms mais il faut qu'il puisse répondre au ping avec ce nom sinon check_mk n'arrivera pas à faire la résolution de nom lors de l'inventaire. - Citation :
- Petite astuce:
Si vous désirez des noms génériques, vous pouvez le faire en renseignant le fichier /etc/hosts de cette manière par exemple:
Extrait de /etc/hosts d'une ubuntu:
127.0.0.1 localhost
xx.xx.xx.xx dev-nagios.mon-domaine.net dev-nagios
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
ff02::3 ip6-allhosts
# Declaration de vos hotes supervises
yy.yy.yy.yy hote-ubuntu
Après ça le ping de hote-ubuntu répondra sous l'IP yy.yy.yy.yy
InventaireNous allons réaliser un nouvel inventaire sur notre serveur nagios pour rapatrier les informations des hôtes supplémentaires.
check_mk -I alltcp - Citation :
- cpu.loads 1 new checks
cpu.threads 1 new checks
df 6 new checks
diskstat nothing new
ipmi nothing new
kernel.util 1 new checks
local nothing new
logwatch nothing new
lsi.array nothing new
lsi.disk nothing new
md nothing new
mem.used 1 new checks
multipath nothing new
netctr.combined 1 new checks
netif.link nothing new
netif.params nothing new
nfsmounts nothing new
oracle_asm_dg nothing new
oracle_asm_disk nothing new
oracle_inst nothing new
oracle_tbs nothing new
services nothing new
statgrab_net.ctr nothing new
statgrab_net.link nothing new
statgrab_net.params nothing new
tsm_stgpool nothing new
vms_df nothing new
vms_md nothing new
vms_netif nothing new
vms_sys.mem nothing new
vms_sys.util nothing new
winperf.cpuusage nothing new
winperf.diskstat nothing new
Ensuite, vérifions si nous arrivons à récupérer les infos pour localhost et hote-ubuntu
- Code:
-
check_mk -nv hote-ubuntu
- Citation :
- CPU load OK - 0.00
CPU utilization OK - user: 0%, system: 0%, wait: 1%
Memory used OK - 19.4% of RAM (23 MB) used by processes
NIC eth0 counters OK - Receive: 0.00 MB/sec - Send: 0.00 MB/sec
Number of threads OK - 31 threads
fs_/ OK - 34.2% used (0.2 of 0.5 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/boot OK - 25.6% used (0.1 of 0.2 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/opt OK - 12.5% used (0.0 of 0.2 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/tmp OK - 6.3% used (0.0 of 0.5 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/usr OK - 13.6% used (0.1 of 1.0 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/var OK - 23.0% used (0.2 of 1.0 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
OK - Agent Version 1.0.35, processed 11 host infos
- Code:
-
check_mk -nv localhost
- Citation :
- CPU load OK - 0.00
CPU utilization OK - user: 3%, system: 1%, wait: 0%
Disk IO read OK - 0.0MB/s (in last 4 secs)
Disk IO write OK - 0.0MB/s (in last 4 secs)
Memory used OK - 14.0% of RAM (70 MB) used by processes
NIC eth0 counters OK - Receive: 0.00 MB/sec - Send: 0.00 MB/sec
Number of threads OK - 49 threads
fs_/ OK - 44.6% used (0.2 of 0.5 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/boot OK - 25.6% used (0.1 of 0.2 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/opt OK - 22.4% used (0.1 of 0.2 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/tmp OK - 6.3% used (0.0 of 0.5 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/usr OK - 33.7% used (0.3 of 1.0 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
fs_/var OK - 36.6% used (0.4 of 1.0 GB), (levels at 80.0/90.0%)
OK - Agent Version 1.0.35, processed 13 host infos
Intégration des check_mk'sEnsuite, ce qui nous intéresse est de pouvoir intégrer de manière simple ces résultats à Nagios.
check_mk -U - Citation :
- Generating Nagios configuration for hosts...OK
Generating Nagios configuration for services...OK
Precompiling host checks...OK
Successfully created Nagios configuration file /opt/nagios/etc/objects/check_mk_objects.cfg.
Please make sure that file will be read by Nagios.
You need to restart Nagios in order to activate the changes.
L'option -U génére les déclarations d'hôtes et de services, vérifie la cohérence des infos et les poussent vers le répertoire /opt/nagios/etc/objects de votre serveur nagios.
Avant de redémarrer Nagios,1) Nous avons réaliser ce test via un serveur nagios vierge
2) Penser à retirer les doublons car check_mk génère des timeperiods, contacts …
Deux options s'offrent à vous :
Soit vous retirez les fichiers de base de votre conf nagios pour laisser place à ceux de check_mk comme ceci :
- Code:
-
vi /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
- Citation :
- #cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg
#cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg
#cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/timeperiods.cfg
#cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/templates.cfg
#cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/localhost.cfg
# Definitions for monitoring a Windows machine
#cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/windows.cfg
# Definitions for monitoring a router/switch
#cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/switch.cfg
# Definitions for monitoring a network printer
#cfg_file=/opt/nagios/etc/objects/printer.cfg
#cfg_dir=/opt/nagios/etc/objects
After the scan, you can automatically add the newly discovered services to Nagios by running the following command:
- Code:
-
check_mk -R
- Citation :
- Generating Nagios configuration...OK
Validating Nagios configuration...OK
Precompiling host checks...OK
Restarting Nagios...OK
Vous pouvez bien sûr tester votre configuration avec
- Code:
-
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Pour finir redémarrer Nagios pour obtenir le résultat comme ci-dessous.
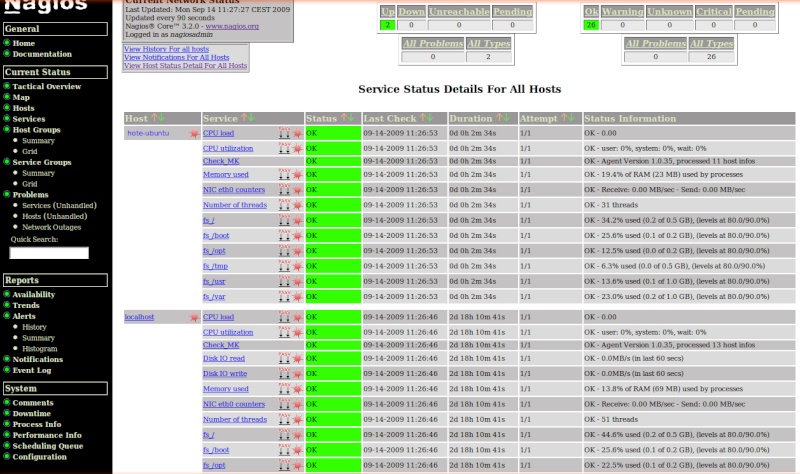
Récap:
A chaque fois que vous aurez un hôte à ajouter,
Installer l'agent check_mk sur votre hôte à superviser
Sur le serveur nagios:
Ajoutez le dans le main.mk
Refaire un inventaire sudo check_mk -I alltcp
Tester si vous arrivez à récupérer vos résultats
Repousser la conf avec l'option -U
Redémarrer Nagios
Y a vraiment beaucoup plus de lecture que de chose à faire, mais c'est bien, un tuto détaillé parfois.
La suite, pnp4nagios






